Anti-corrosion AlN ceramic crucible with excellent thermal shock resistance for induction melting of TiAl alloy
Ruyuan Wang, Chao Zhao* , Xiaotao Liu, Minghan Sun, Ning Li*
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272884223025099
Abstract
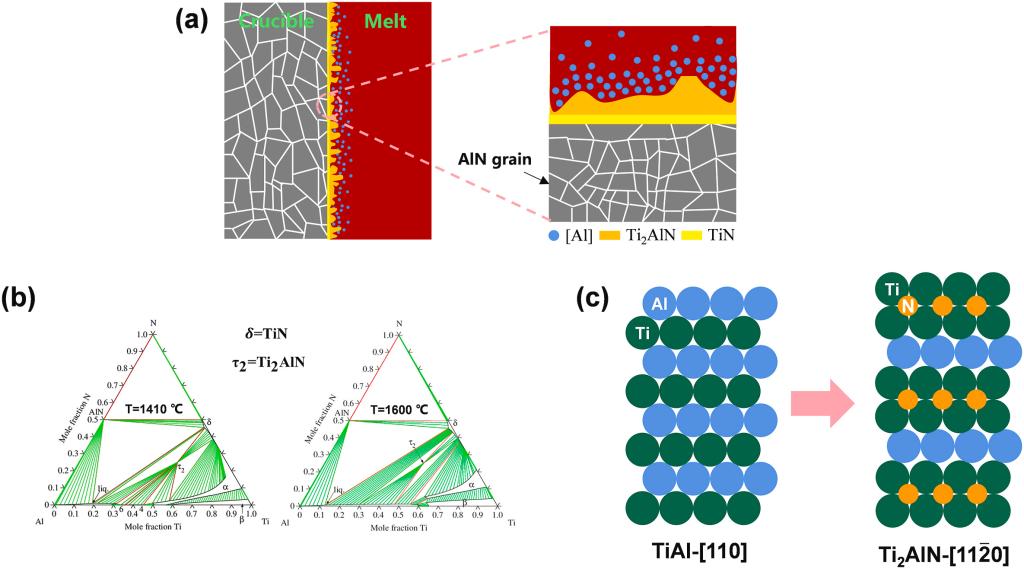
Molten Ti possesses significantly high chemical activity, causing it to react with crucible materials; this renders the induction melting of Ti alloys extremely challenging. Therefore, fabricating effective and inexpensive crucibles suitable for this process is vital. In this study, an aluminum nitride ceramic crucible with excellent TiAl-induction-melting performance was manufactured. TiAl alloys melted in this crucible showed high purity with an ultra-low oxygen content (<0.1 wt%), and the melting process involved negligible crucible/metal interactions. Subsequently, the performance of the AlN crucible was systematically investigated, with particular emphasis on its anti-corrosion mechanism. The excellent induction-melting performance of the crucible could be ascribed to the formation of a dense TiN barrier film and an Al-rich layer on the crucible surface during melting. The following interfacial reaction (predicting the generation of both TiN and Al-rich phases) was proposed: 3TiAl (l) + 2AlN (s)→TiN + Ti2AlN + 4TiAl [Al]. This study provides an in-depth understanding of the fabrication and physical properties of AlN crucibles, which can aid future research on the induction melting of Ti-based alloys.